Unveiling the Rich Tapestry of Indian History: Significance of Sikh Contributions

Indian history stands as a testament to the vibrant cultural, social, and political evolution that has fashioned the subcontinent for millennia. Among the many threads which have woven this complicated tapestry, the contributions of Sikhism have left an indelible mark. From the status quo of the Sikh Empire to their role in the combat for independence, Sikh records are a quintessential part of Indian history that holds priceless classes for students in schools and colleges.
 Also see: tech news latest: Unveiling the Surge of Online Scams in India
Also see: tech news latest: Unveiling the Surge of Online Scams in India
The Emergence of Sikhism:
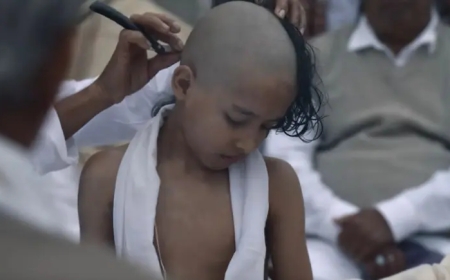
Sikhism, founded in the late fifteenth century by using Guru Nanak Dev Ji, emerged as an awesome faith that harmonized factors from Hinduism and Islam even advocating for social justice, equality, and selfless carrier. The Sikh Gurus, numbering ten overall, no longer most effectively propagated non-secular teachings but additionally actively challenged the socio-political norms of their time.Sikh Contributions to Indian History:
1. The Sikh Empire: Under the management of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, the Sikh Empire flourished in the early nineteenth century, spanning across areas in present-day India and Pakistan. The empire's cultural richness, architecture, and inclusive policies stand as a testimony to the Sikh spirit. 2. Role in Indian Independence: Sikhs played a massive function in India's fight for freedom against British colonial rule. Prominent figures like Bhagat Singh, Udham Singh, and Lala Lajpat Rai have been Sikh patriots who sacrificed their lives for the U. S . A .'s liberation. 3. Empowerment of Women: Sikh history boasts inspirational testimonies of women warriors like Mata Bhag Kaur, who led troops in battles. Sikhism's emphasis on equality and empowerment allowed ladies to interrupt societal norms and end up leaders. 4. Humanitarian Values: The idea of langar, a free network kitchen, installed through Guru Nanak, exemplifies Sikhism's recognition of seva (selfless provider) and imparting for the needy, transcending non-secular barriers. 5. Religious Freedom: Sikhs were robust advocates of non-secular freedom, obvious from the records of the development and upkeep in their holy places, which includes the Golden Temple in Amritsar. Also see: tech news latest: Unveiling the Surge of Online Scams in India
Also see: tech news latest: Unveiling the Surge of Online Scams in India