Data Privacy and Protection in India: Navigating the Complexities of the Digital Age
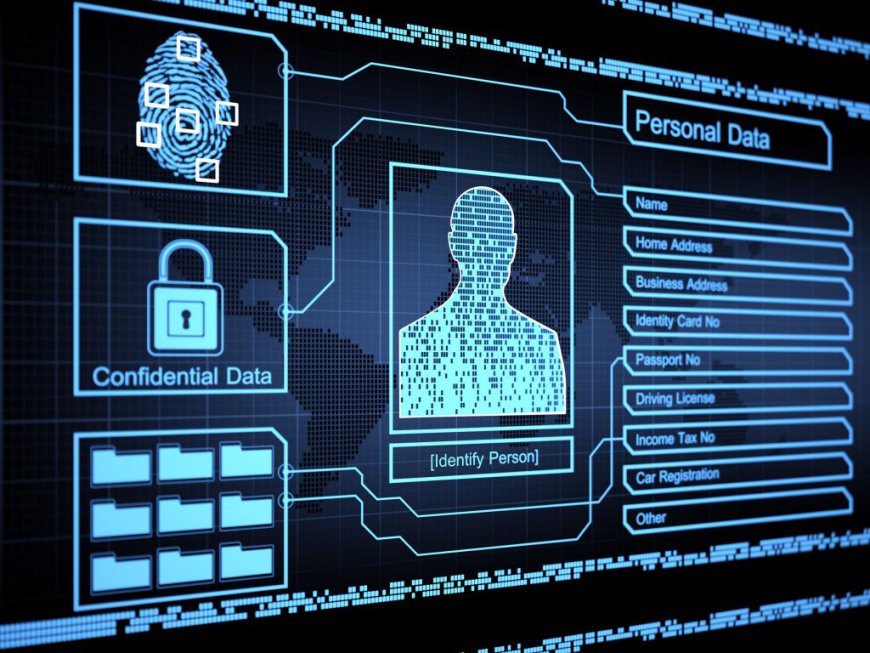

In the era of digitization, data has become a valuable currency, driving innovation, personalized experiences, and business growth. However, as data proliferates, so do concerns regarding its privacy and protection. In India, safeguarding data privacy has emerged as a critical issue that requires careful navigation through the complexities of the digital age. This article explores the challenges, regulatory landscape, and best practices for data privacy and protection in India, highlighting the need for a comprehensive approach to ensure the security and trustworthiness of personal information.


The Evolving Landscape of Data Privacy
With the advent of smartphones, social media, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, personal data has become increasingly vulnerable to misuse and unauthorized access. The rapid growth of digital services and the collection of vast amounts of user data have raised concerns about data breaches, identity theft, and intrusive surveillance. It is imperative to strike a balance between utilizing data for innovation while upholding individuals' right to privacy.Regulatory Framework and Legal Safeguards
In recent years, India has made significant strides in data privacy legislation. The introduction of the Personal Data Protection Bill aims to establish a robust framework for protecting individuals' personal information. The bill outlines guidelines for consent management, data localization, data breach notifications, and the establishment of a Data Protection Authority. These regulatory measures play a crucial role in creating a legal framework that promotes transparency, accountability, and user control over their data.Challenges and Considerations
Implementing effective data privacy measures is not without its challenges. Rapid technological advancements, cross-border data flows, and the vast amount of data generated present complex hurdles. Ensuring data privacy requires addressing technical, organizational, and cultural challenges. Organizations must adopt encryption, authentication, and access control measures to protect sensitive data. Building a privacy-aware culture that emphasizes data ethics, employee awareness, and training is equally important.Data Localization and Cross-Border Data Transfers
The debate surrounding data localization and cross-border data transfers adds another layer of complexity to data privacy in India. While data localization aims to protect sensitive information, it can also impact international collaborations, hinder innovation, and increase compliance costs. Striking the right balance between data sovereignty and global data flows requires thoughtful consideration and international cooperation.Read more: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Advancing Medical Outcomes